The inportant of “breathing” and “oxygen”
1.The source of energy: the “engine” that drives the body
This is the core function of oxygen. Our bodies need energy to perform all activities, from heartbeat, thinking to walking and running.
2.Maintaining basic physiological functions: the bottom line of survival
The body has many critical functions that are performed all the time and are completely dependent on a continuous supply of energy, which cannot be achieved without oxygen.
- Brain function: The brain is the body’s headquarters. Although it only accounts for 2% of body weight, it consumes 20%-25% of the body’s oxygen. After just a few minutes of oxygen deprivation, brain cells begin to damage, leading to dizziness, confusion, and even permanent damage.
- Heartbeat: The heart is a muscle that works constantly, pumping oxygenated blood throughout the body. The heart muscle itself requires a large amount of oxygen to maintain its contraction. Lack of oxygen can lead to heart rhythm disorders, angina, and even myocardial infarction (heart attack).
- Metabolism: All the chemical processes in the body that sustain life, such as digesting food, repairing tissues, and eliminating waste, require energy to drive and therefore indirectly rely on oxygen.
3.Maintaining internal environment stability: the body’s “master of balance”
Oxygen is essential for maintaining a stable chemical environment within the body.
- Acid-base balance: Cellular metabolism produces acidic waste products (such as carbonic acid). Oxygen helps maintain the pH of blood and body fluids within a narrow, stable range, which is necessary for enzymes and cells to function properly.
- Immune defense: The human immune system, particularly certain immune cells (such as macrophages), produces large amounts of highly oxidizing “reactive oxygen species” as weapons when engulfing and destroying bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. The efficiency of this process is closely related to oxygen levels.
For those who need additional oxygen support, traditional oxygen tanks are bulky, require replacement, and pose safety risks. So, is there a more convenient and sustainable solution?
Yes, that’s an oxygen concentrator – a smart device that extracts oxygen from the air around us.“Think of an oxygen concentrator as a very smart air filter. It takes in regular air, filters out the unwanted gases, and leaves you with medical-grade oxygen for you to breathe.”
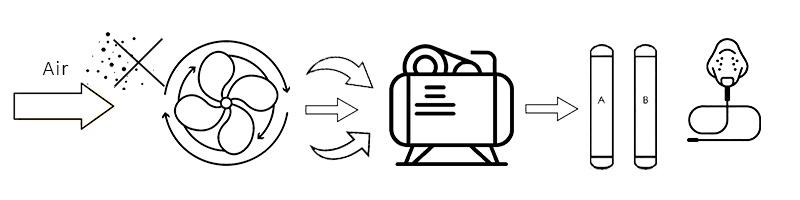
The “organ” of the oxygen concentrator
1. Air filter: The “first line of defense,” responsible for removing dust, allergens and other particles from the air.
2.Compressor: The “heart of the machine”, responsible for pressurizing the inhaled air.
3.Molecular sieve: The “magic part,” filled with special particles called zeolites that adsorb nitrogen extremely well.
4. Gas storage tank/buffer tank: used to store purified oxygen to make the airflow output more stable.
5. Flow meter and nasal oxygen cannula: User control interface used to adjust the required oxygen flow and deliver oxygen to the user.
The magic of “air turning into oxygen”
1.Inhalation and filtration
The machine draws in ambient air from the room (approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen).Just like we take a deep breath.
2.Compression
The compressor pressurizes the sucked air,Prepare for the next separation process.
3.Separation
Pressurized air is fed into the molecular sieve column,The zeolite particles act like a powerful “nitrogen magnet,” attracting nitrogen molecules in the air while allowing smaller oxygen molecules to pass through.What is output from the other end of the molecular sieve is oxygen with a concentration of up to 90%-95%.
4.Output and loop
(Output oxygen): High-purity oxygen is fed into a gas tank and then delivered to the user through a flow meter and nasal oxygen cannula.
(Nitrogen Exhaust): Simultaneously, another molecular sieve tower releases the adsorbed nitrogen (which is harmless) back into the air by reducing the pressure. The two towers cycle through pressure swing adsorption technology, ensuring a continuous output of oxygen.
It’s like two workers taking turns working, one filtering the air while the other cleans up the “garbage” (nitrogen), thus achieving 24/7 uninterrupted oxygen supply.
Pulse Flow vs. Continuous Flow
1.Continuous Flow: Continuously delivers oxygen like an uninterrupted stream. Ideal for sleeping or users who require continuous oxygen delivery.
2.Pulse Flow: Intelligent mode. A burst of oxygen is delivered only when the user inhales. This is more energy efficient and significantly extends the battery life of the portable oxygen concentrator.
Important safety tips
1.Oxygen concentrators provide concentrated oxygen, not pure oxygen. This is safe and meets medical standards.
2.Always consult your doctor before using any oxygen concentrator. Your doctor will tell you whether you need supplemental oxygen, as well as the required flow rate (LPM) and oxygen saturation target.
3.Maintain adequate ventilation around the device and clean or replace filters regularly to ensure optimal performance.
Post time: Oct-17-2025